For decades, our interaction with digital worlds has been a conversation conducted through a thick pane of glass. We could see the stunning vistas and hear the roaring dragons, but we could never truly feel them. The primary form of physical feedback has been the crude, imprecise rumble of a controller—a technology that, while revolutionary in the 90s, feels archaic in 2025. But that pane of glass is now shattering. We are standing on the precipice of a new era, a fundamental shift in how we experience interactive entertainment. This is the haptic gaming revolution, a movement poised to transform games from a purely audiovisual medium into a full-body, sensory experience.
This is not a distant, science-fiction dream. The technology is here, rapidly maturing and integrating into the gaming ecosystem. Haptics are moving beyond simple vibrations to deliver a rich, textured language of touch that can communicate everything from the subtle pitter-patter of rain on a jacket to the bone-jarring impact of a shockwave. This revolution is about erasing the final barrier between the player and the game world, creating a level of immersion and presence that was previously unimaginable.
This definitive guide will explore every facet of the coming haptic revolution. We will dissect the cutting-edge hardware, from advanced controllers to full-body suits, that is making this possible. We will analyze the software and development tools that allow creators to build these tactile worlds, examine the profound impact this technology will have on gameplay across all genres, and look ahead to the future of truly feeling our virtual realities. Prepare to go beyond the rumble.
The Evolution from Vibration to Sensation
To understand where we are going, we must first appreciate where we’ve been. The journey of haptics in gaming began with simple, eccentric rotating mass (ERM) motors. These motors, found in controllers like the Nintendo 64’s Rumble Pak and the original PlayStation DualShock, created vibrations by spinning an off-balance weight. While effective for conveying large impacts like explosions or crashes, they were a blunt instrument, incapable of nuance.
The first major leap forward came with the introduction of Linear Resonant Actuators (LRAs). Technologies like Nintendo’s “HD Rumble” in the Switch Joy-Cons and Sony’s “Haptic Feedback” in the PlayStation 5’s DualSense controller utilize LRAs. These actuators can start and stop with incredible speed and precision, allowing them to generate a vast range of highly defined frequencies and amplitudes. This is the difference between a sledgehammer and a surgical scalpel. An LRA can replicate the feeling of individual raindrops, the tension of a bowstring being pulled, or the distinct texture of walking across different surfaces like sand, gravel, or metal.
The DualSense controller, in particular, served as the mainstream proof-of-concept for this new generation of haptics. Its adaptive triggers, which can create variable tension and resistance, combined with its detailed feedback, demonstrated to millions of players that haptics could be more than just a gimmick; they could be a core part of the gameplay experience. But even this is just the beginning. The true revolution lies in extending this sensory fidelity beyond the hands and across the entire body.
The Hardware: Pillars of the Haptic Ecosystem
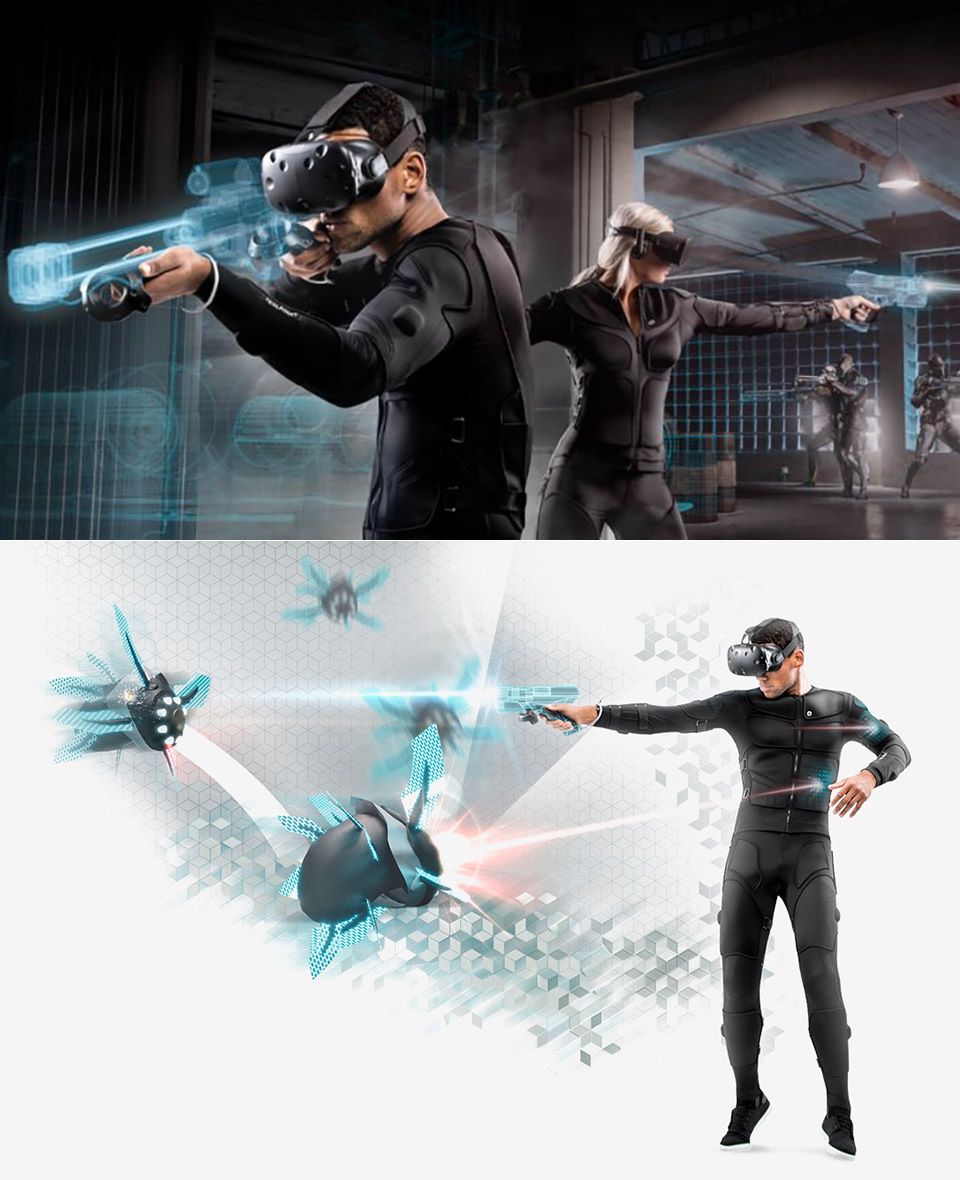

The modern haptic revolution is being built upon a diverse ecosystem of specialized hardware. Each component is designed to immerse a different part of the body, working in concert to create a complete sensory illusion. As of 2025, these are the key pillars driving the movement forward.
A. Advanced Haptic Vests and Suits: This is where the most significant advancements are taking place. Companies like Teslasuit and bHaptics have pioneered full-upper-body vests and, in some cases, complete suits, embedded with dozens of individual haptic actuators. These are not simple rumble vests. Each actuator can be controlled independently, allowing for highly detailed, location-based feedback.
- Directional Feedback: Feel the precise location of an enemy’s bullet impact—a sharp tap on your left shoulder blade, a slash across your chest. This provides invaluable tactical information beyond a simple on-screen indicator.
- Environmental Immersion: Experience the ambient sensations of the world. Feel the subtle pressure of wind pushing against you, the warmth of a nearby fire radiating onto your chest, or the ripple of a magical spell washing over your body.
- Force Simulation: Paired with electro-muscle stimulation (EMS) in high-end suits, this technology can create involuntary muscle contractions, simulating the g-force of accelerating in a race car or the physical strain of lifting a heavy object.
B. Haptic Gloves and Tactile Feedback: While controllers immerse the palms, haptic gloves aim to bring sensation to the fingertips, a crucial step for true VR and AR interaction. These gloves use a combination of technologies, including micro-LRAs in each finger, to simulate the feeling of touching objects. More advanced systems incorporate pneumatic bladders or microfluidic systems that can create pressure and resistance, allowing you to “feel” the shape, texture, and hardness of a virtual object. Imagine picking up a virtual stone and feeling its weight and rough texture, or resting your hand on a wooden table and sensing the grain. This technology is the key to making virtual hands feel like your own.
C. Subsonic and Bass Haptics: This category of hardware focuses on the low-frequency vibrations that we feel as much as we hear. Devices like the SubPac, which can be worn as a backpack or integrated into a chair, translate the bass frequencies from a game’s audio into powerful, deep vibrations that resonate through the user’s entire body. This is perfect for feeling the thud of nearby footsteps, the deep rumble of a tank engine, or the powerful beat of music in a rhythm game. It adds a visceral, physical weight to the soundscape that headphones and speakers alone cannot provide.
D. The Software and Development Layer: Hardware is useless without sophisticated software to control it. The revolution is being accelerated by the development of standardized haptic design tools and plugins for major game engines like Unreal Engine and Unity. SDKs (Software Development Kits) from companies like Lofelt and Interhaptics allow developers to easily author complex haptic signals and map them to in-game events. Instead of programming each individual motor, a developer can simply say “create a ‘rain’ effect” or “design a ‘sword slash’ sensation,” and the software translates that into a detailed signal compatible with a wide range of haptic hardware. This democratization of haptic design is crucial for widespread adoption.
The Impact on Gameplay: Redefining Genres
Haptic technology is not a one-size-fits-all solution; its impact will be felt differently across various genres, fundamentally deepening the player experience in unique ways.
- First-Person Shooters (FPS): The most obvious application. Haptic vests provide critical directional feedback, changing how players react to threats. The distinct kick of each weapon, the subtle vibration of a nearby grenade, and the impact of suppression fire all become part of the tactical landscape.
- Racing and Flight Simulators: Full-body haptics and subsonic transducers create an unparalleled sense of connection to the vehicle. You can feel the texture of the road through your seat, the loss of traction as you drift around a corner, the g-force pushing you back during acceleration, and the buffeting of turbulence in the air.
- Horror Games: Haptics are a powerful tool for building tension and delivering scares. Imagine feeling the faint, skittering footsteps of an unseen creature behind you, the cold touch of a ghostly presence, or the startling jolt of a jump scare resonating through your entire body. It bypasses the analytical part of the brain and targets a primal, physical fear response.
- Role-Playing Games (RPG) & Adventure: Haptics will enrich world-building and narrative. Feel the crackle of magical energy in your hands as you cast a spell, the ancient rumble of a dungeon’s secret door opening, or the unique sensation of a character placing a key item into your virtual palm.
- Accessibility: Haptics offer transformative potential for gamers with hearing impairments. Complex audio cues—such as enemy callouts, environmental warnings, or musical shifts—can be translated into distinct tactile signals, providing a rich layer of information that was previously inaccessible.
The Challenges Ahead: Overcoming the Hurdles

Despite the incredible potential, the path to mainstream adoption is not without its challenges.
- Cost: High-end haptic suits and gloves remain prohibitively expensive for the average consumer, often costing thousands of dollars. While prices are falling, reaching a sub-$500 price point for a quality vest is the next major milestone needed for mass-market appeal.
- Standardization: The ecosystem is currently fragmented. A haptic effect designed for a bHaptics vest may not work on a Teslasuit. The industry needs to coalesce around universal standards and APIs so developers can “create once, deploy everywhere.”
- The “Killer App”: Like any new hardware, the haptic ecosystem needs its Half-Life: Alyx—a must-play, AAA title designed from the ground up around haptic immersion. A major studio needs to invest heavily in the technology to showcase its full potential and drive hardware sales.
- Haptic Design as an Art Form: Creating meaningful haptics is a new and complex skill. Poorly designed haptics can be distracting, annoying, or even lead to sensory overload. The industry needs to cultivate a new class of “Haptic Designers” who understand the language of touch as well as sound designers understand audio.
Conclusion: The Future is Tangible
The haptic gaming revolution is here, and it is gaining momentum with each passing day. We are rapidly moving beyond the age where games are merely things we see and hear. They are becoming worlds we can touch, environments we can feel, and experiences that engage our entire bodies. The journey from the simple rumble of a single motor to the complex symphony of a full-body haptic suit marks a pivotal moment in the history of interactive entertainment.
The challenges of cost and standardization are significant but not insurmountable. As the technology becomes more affordable and the development tools more powerful, the barrier between our physical selves and our digital avatars will continue to dissolve. The result will be a new golden age of immersion, where the stories games tell are not just witnessed, but are felt in our very bones. The future of gaming is tangible, and it promises an experience more profound and believable than we ever thought possible.